imixs-cloud
Firewall Setup
As mentioned in the architecture overview you can run your cluster within the public Internet and without using a second private network. Setup with only one public network reduces complexity which is always an advantage. But you need to protect your cluster in this case (and you should do this also when you have a private network).
The goal of the following Firewall setup rule is to avoid unauthorized access to your cluster but allowing internal communication. Kubernetes has a lot of ports needed for internal communication which should not be accessible form outside your environment.
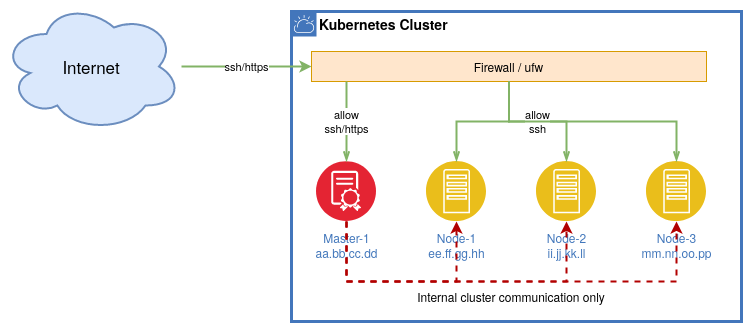
The only necessary ports to be opened from outside are :
22 – SSH
443 – HTTPS access
To protect your cluster you can use the firewall tool ufw. You should familiarize yourself with the ufw tool to prevent you from locking yourself out of your server.
As we want to allow communication only internally we need to restrict public access to port 22 (ssh) and 443 (https). All other incoming traffic can be blocked. Assuming you public Nodes have the following public Internet addresses:
master-1 aa.bb.cc.dd
worker-1 ee.ff.gg.hh
worker-2 ii.jj.kk.ll
worker-3 mm.nn.oo.pp
you can do run the following setup_ufw.sh bash script on each node to protect access from outside:
$ ./setup_ufw.sh
This is an example script with a rule set with a example rule set.
ufw allow ssh comment 'allow ssh access form anywhere'
ufw allow 443 comment 'allow https only'
# allow internal communication only
ufw allow from aa.bb.cc.dd
ufw allow from ee.ff.gg.hh
ufw allow from ii.jj.kk.ll
ufw allow from mm.nn.oo.pp
# Allow all outgoing
ufw default allow outgoing
ufw default deny incoming
ufw enable
See the setup_ufw.sh bash script in the /scripts directory.
After activating your firewall, you can verify the status with:
$ sudo ufw status verbose
Note: You need to repeat the step on each node.
To disable the firewall run:
$ sudo ufw disable
Changing Rule Set
To change the rules (e.g. adding a new cluster node) you simply need to edit your setup_ufw.sh bash script and run the setup once again.
Note: Adding a new role can be done easily with the ufw allow command. But to remove all old rules you need to run ufw reset first and than add all rules once again. The setup_ufw.sh bash script does this automatically.
# Remove all existing rules
$ sudo ufw reset
# Rebuild all rules
$ ./setup_ufw.sh
# Verify rules
$ sudo ufw status verbose